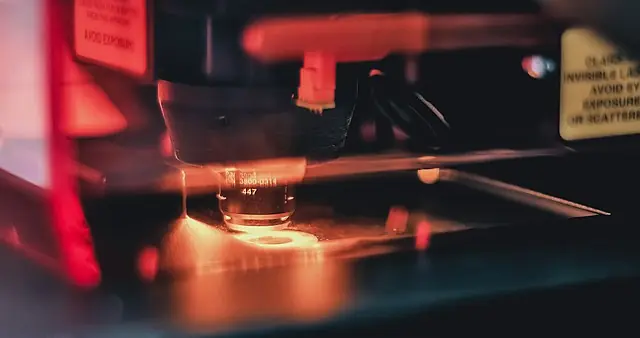
What is Laser Marking used for?

Laser marking technology continues to play a critical role in various industries, from product identification to traceability and branding. Utilizing a laser beam to create permanent marks on an array of materials including metal, plastic, glass, and ceramics, the marks can range from text, logos, barcodes, and serial numbers.
In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of laser marking, including the various types of lasers utilized, the materials that can be marked, and the distinct methods of laser marking. Additionally, we shed light on the inner workings of laser marker machines and how they produce accurate and permanent marks on materials.
To grasp the concept of laser marking, it is crucial to familiarize oneself with the different types of lasers used in the process. Currently, there are several types of lasers in use including CO2, YAG, and fiber lasers. CO2 lasers are the most widely used type of laser for marking and engraving, renowned for their versatility and ability to mark a broad range of materials. YAG lasers, on the other hand, are recognized for their high precision and capacity to mark small and intricate areas. Fiber lasers are the latest addition to laser marking technology, well-known for their high speed and ability to mark an extensive range of materials.
In addition to understanding the types of lasers, it’s imperative to comprehend the materials that can be marked using laser marking technology. The process can be applied to various materials such as metals (steel, aluminum, and titanium), plastics, ceramics, and glass. The type of laser used will determine the materials that can be marked, with some lasers being more suitable for specific materials than others. For instance, CO2 lasers are more suitable for marking plastics and ceramics, while YAG lasers are better suited for marking metals.
Laser marking also includes various methods such as engraving, annealing, and ablation. Engraving is the process of utilizing a laser beam to remove material from the surface of a material, creating a precise and permanent mark. Annealing uses a laser beam to heat the surface of a material, creating a visible mark without removing any material. Ablation is a process that uses a laser beam to vaporize a small amount of material, creating a precise and permanent mark.
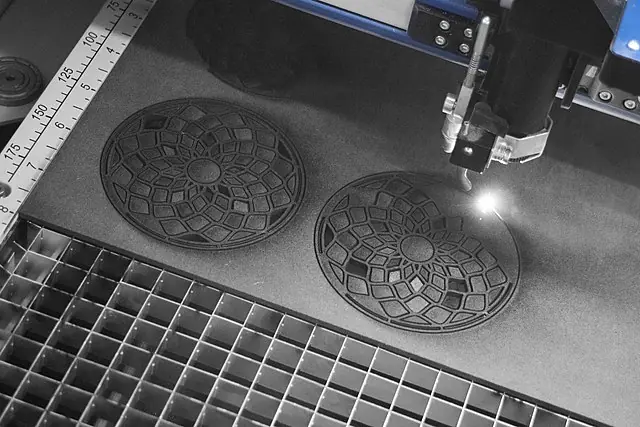

A laser marker machine typically consists of several components, including a laser, a beam delivery system, a controller, and a material handling system. The laser generates the beam of light that will be used to mark the material, while the beam delivery system directs the beam of light to the material. The controller is responsible for controlling the laser and the beam delivery system, and the material handling system holds the material in place while it is being marked.
When a material is placed into the laser marker machine, the controller sends a signal to the laser to turn on and begin generating the beam of light. The beam delivery system directs the beam of light to the material, where it creates the mark. The material handling system holds the material in place while the laser is marking, ensuring that the mark is precise and accurate.
In conclusion, laser marking technology is a reliable and efficient method of creating permanent marks on an array of materials. With several types of lasers in use, including CO2, YAG, and fiber lasers, and several methods of laser marking, including engraving, annealing, and ablation, the technology continues to play a critical role in various industries. Understanding the inner workings of laser marker machines and their components will give a better understanding of how this innovative technology produces precise and accurate marks.