Dye Lasers

A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as its gain medium. The dye is usually dissolved in a solvent, such as ethanol, and is pumped by a laser beam to produce laser action. The wavelength of the laser light is determined by the properties of the dye, and can be tuned by changing the dye.
Dye lasers were some of the first lasers to be developed, and were used extensively in early research on lasers. They are now used in a wide range of applications, including medical diagnosis and treatment, materials processing, and scientific research.
The operating principle of a dye laser is relatively simple. The laser beam pumps energy into the dye molecules, which then fluoresce, or emit light. The emitted light is amplified by stimulated emission, and the laser beam is produced.

The wavelength of the laser light is determined by the properties of the dye molecules. The dye molecules can be designed to absorb light at a specific wavelength, and then emit light at a different wavelength. By carefully selecting the dye molecules, the wavelength of the laser light can be tuned over a wide range.
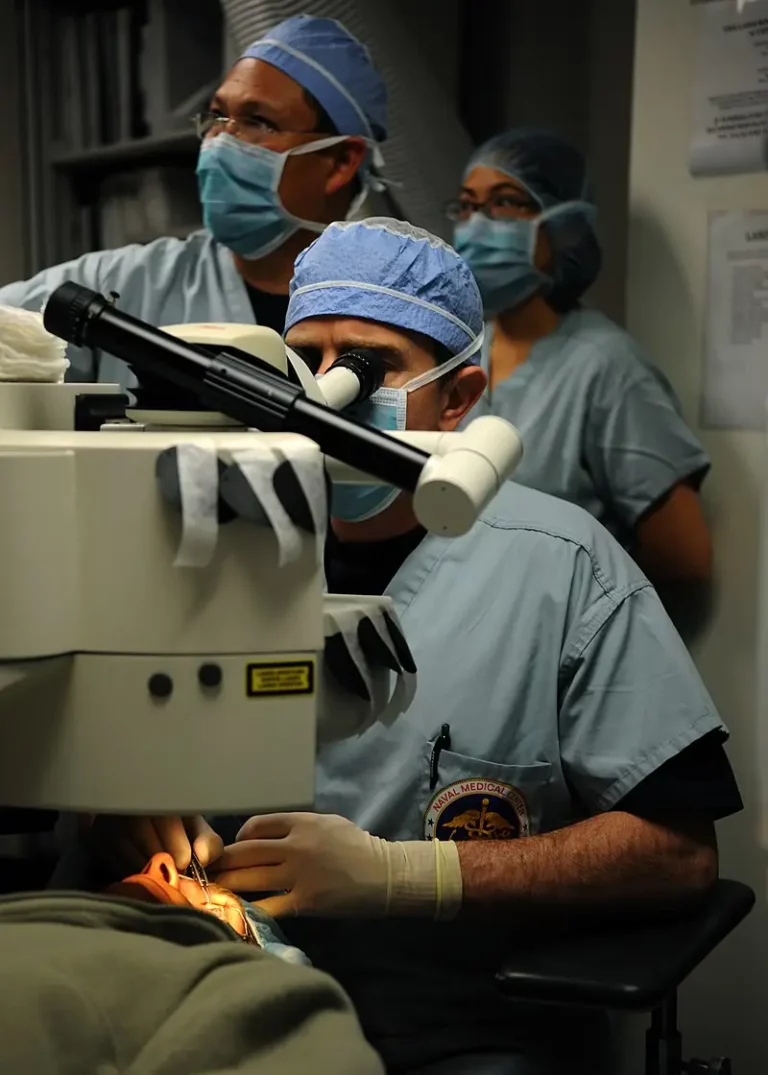
Dye lasers are used in a wide range of applications. They are particularly well suited for medical applications, due to their ability to produce laser light at specific wavelengths. Dye lasers are used for medical diagnosis, such as cancer detection, and for treatment, such as laser surgery.
Dye lasers are also used in materials processing. They are used to cut and weld materials, and to drill holes. Dye lasers can also be used to write and read data on optical discs.
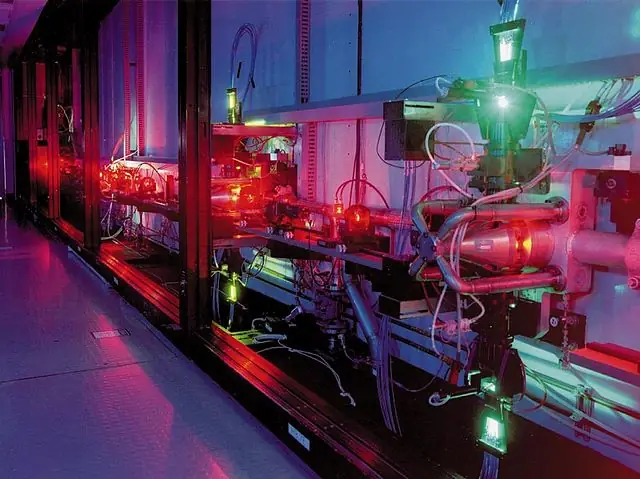
Dye lasers are also used extensively in scientific research. They are used to study the properties of materials, and to investigate the fundamental principles of physics. Dye lasers are also used to generate high-intensity laser beams for experiments in nuclear fusion and other areas of research.
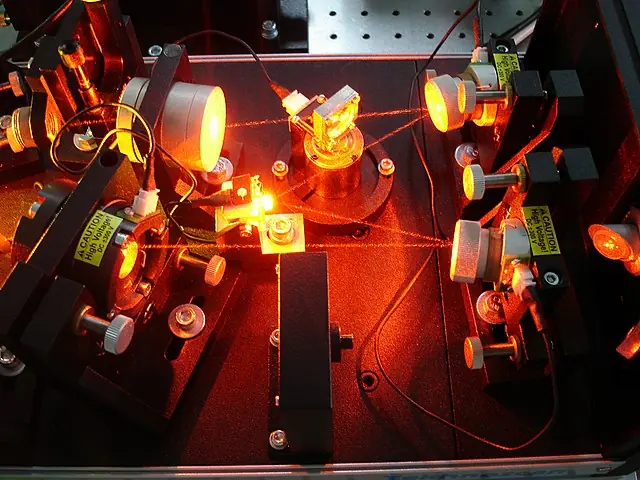
Dye lasers are used in a wide range of applications. They are particularly well suited for medical applications, due to their ability to produce laser light at specific wavelengths. Dye lasers are used for medical diagnosis, such as cancer detection, and for treatment, such as laser surgery.
Dye lasers are also used in materials processing. They are used to cut and weld materials, and to drill holes. Dye lasers can also be used to write and read data on optical discs.
Dye lasers are also used extensively in scientific research. They are used to study the properties of materials, and to investigate the fundamental principles of physics. Dye lasers are also used to generate high-intensity laser beams for experiments in nuclear fusion and other areas of research.