Structural Color Printing: The Future of Digital Printing Technology
A new laser printing technique offers wide-gamut, high-resolution, and high-speed printing with long-term stability and viewing-angle independence.
Optics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior and properties of light and its interaction with matter.
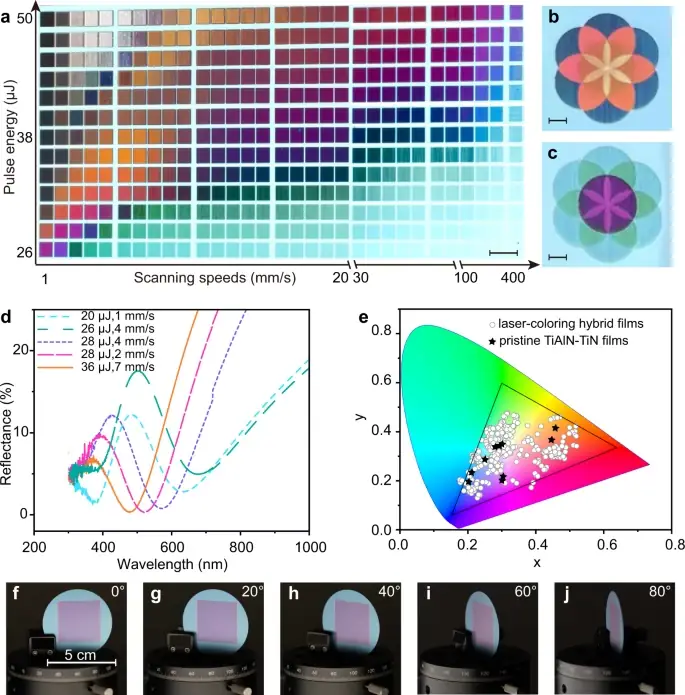
A new laser printing technique offers wide-gamut, high-resolution, and high-speed printing with long-term stability and viewing-angle independence.
Two-photon excitation, a unique form of light-matter interaction in which two photons are absorbed simultaneously by a material, is one such interaction that has a wide range of applications.
In this article, we will explore the various types of beam splitters, how they work, and their applications.

Non-linear optics is a branch of optics that deals the interaction between light and matter, and the ways in which the behavior of light can be altered or controlled through the use of various materials and techniques.
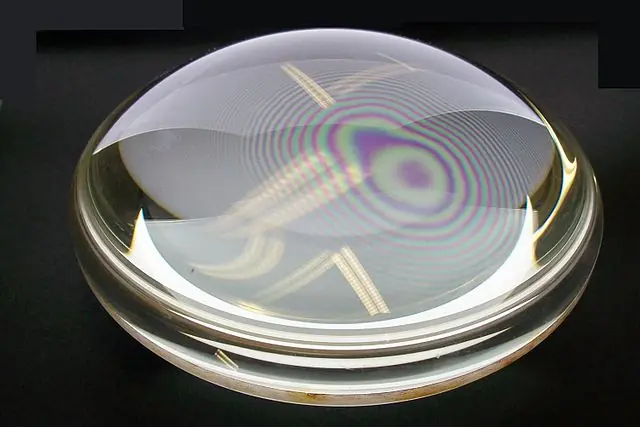
Newton’s rings are an optical phenomenon that occurs when light reflects off a thin film of air or other transparent substance between two surfaces.
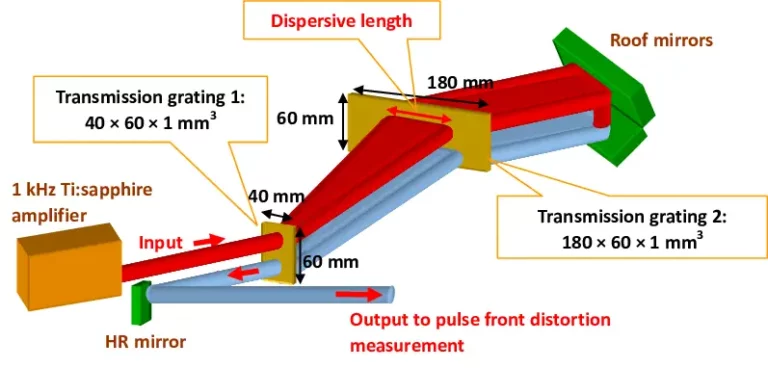
Pulse compression gratings are optical devices used to modify the temporal characteristics of a light pulse.
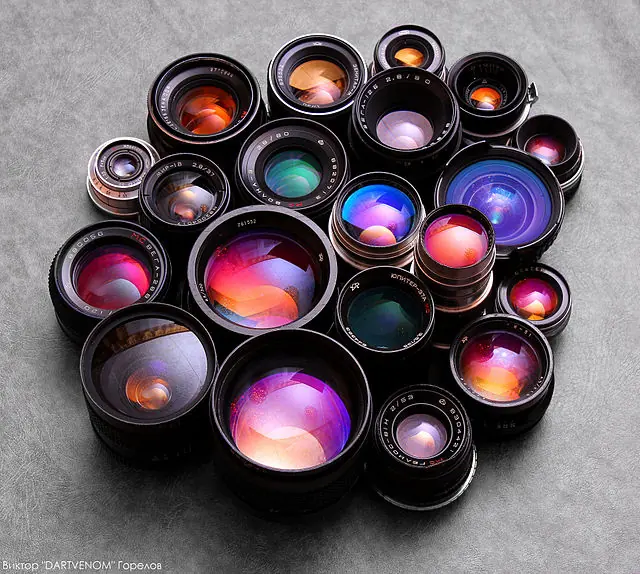

An anti-reflective coating, also known as an AR coating or non-reflective coating, is a thin layer of material applied to the surface of a lens or other optical element in order to reduce the amount of light that is reflected off of it.
A laser etalon is a device that is used to accurately measure the frequency of a laser beam. It works by using the principle of interference, which occurs when two waves meet and either reinforce or cancel each other out.
Gradient-index (GRIN) optics are a type of optical technology that uses lenses or optical fibers with a refractive index that varies in a continuous and gradual manner.
A monochromator is a device used to select and isolate a single wavelength of light from a broader spectrum.
End of content
End of content