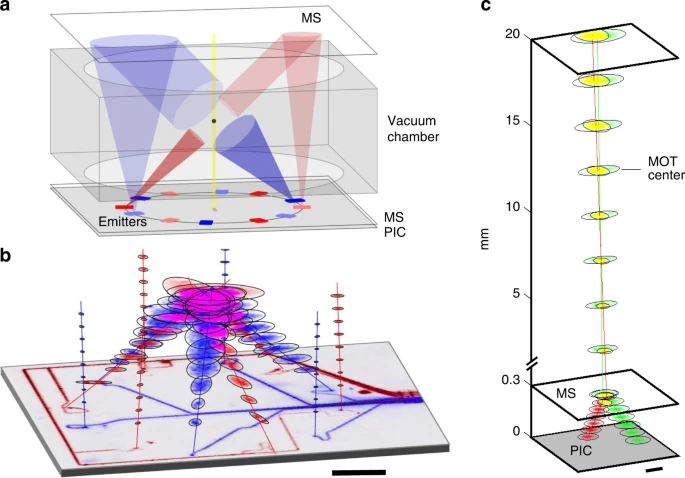
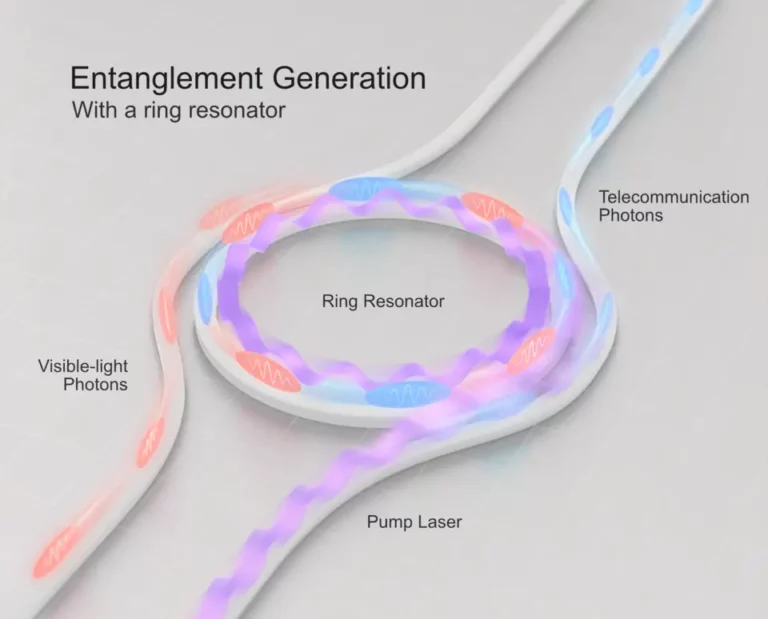
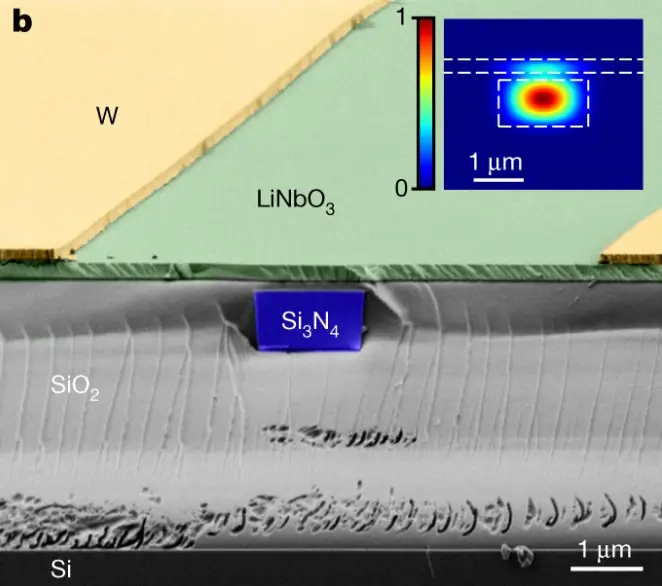
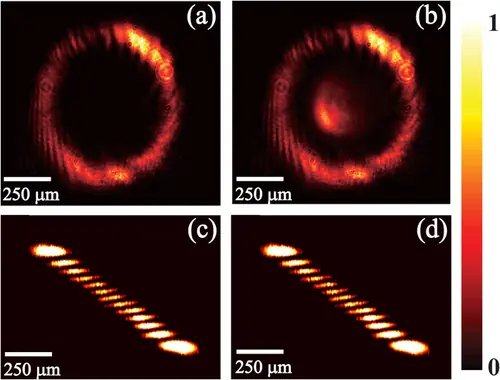
Compact Photonic Chip System Brings Miniaturized Atomic Clocks Closer to Reality
Researchers have developed a groundbreaking compact photonic chip system that paves the way for miniaturized strontium atomic clocks. The achievement has significant implications for atomic technologies, as miniaturization could lead to a range of benefits in applications such as GPS and communication systems.