Polarizing and non-polarizing beamsplitter cubes
Polarizing beamsplitter cubes (PBSCs) and non-polarizing beamsplitter cubes (NPBSCs) are optical devices that are used to split an incoming light beam into two separate beams.
Information about lasers in laboratory uses ranging from spectroscopy and interferometry to ultraviolet fluorescence.
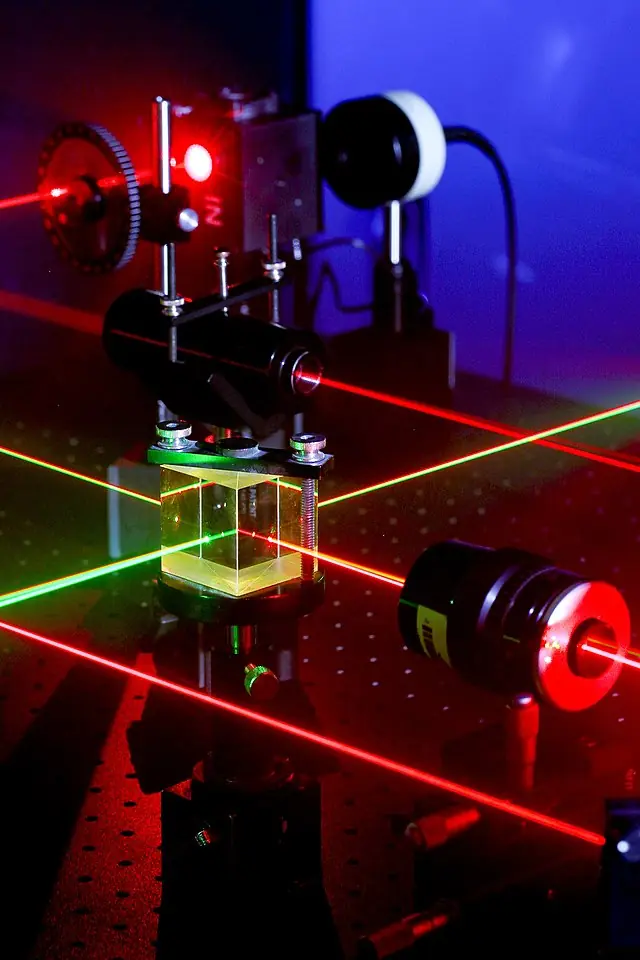
Polarizing beamsplitter cubes (PBSCs) and non-polarizing beamsplitter cubes (NPBSCs) are optical devices that are used to split an incoming light beam into two separate beams.
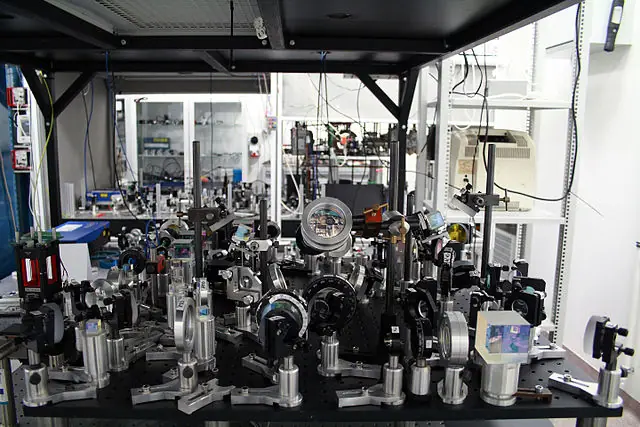

Laser cooling is a technique used to lower the temperature of a system or material using lasers, often close to absolute zero (-273.15°C).
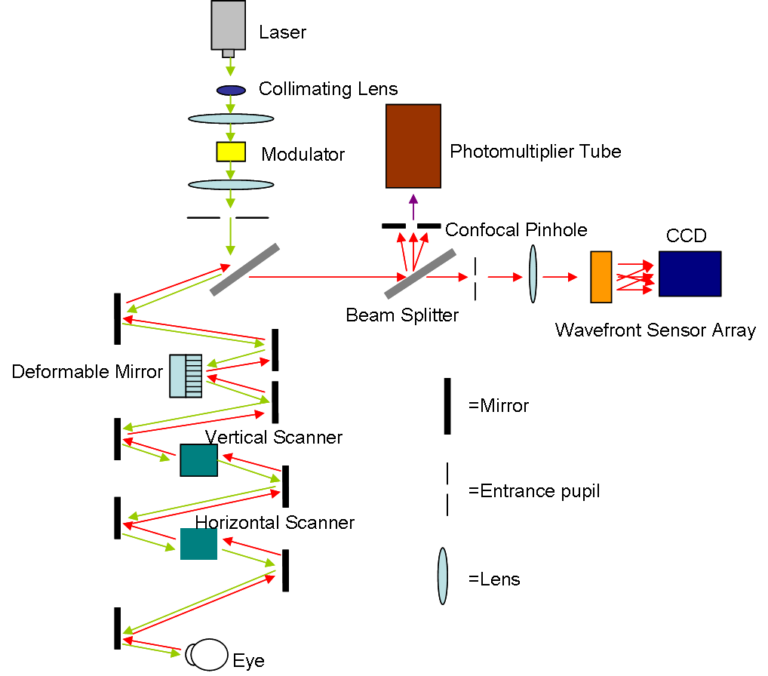
Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (SLO) is a cutting-edge imaging technique used to examine the retina and other structures in the eye.

A dye laser is a laser that uses an organic dye as its gain medium. The dye is usually dissolved in a solvent, such as ethanol, and is pumped by a laser beam to produce laser action. The wavelength of the laser light is determined by the properties of the dye, and can be tuned by changing the dye.
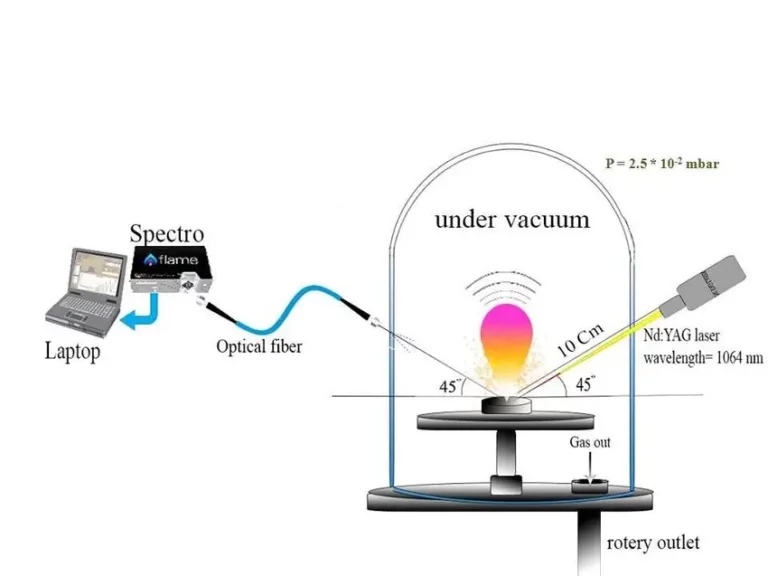
This article provides an overview of Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS), a powerful spectroscopic technique used to analyze the elemental composition of materials.
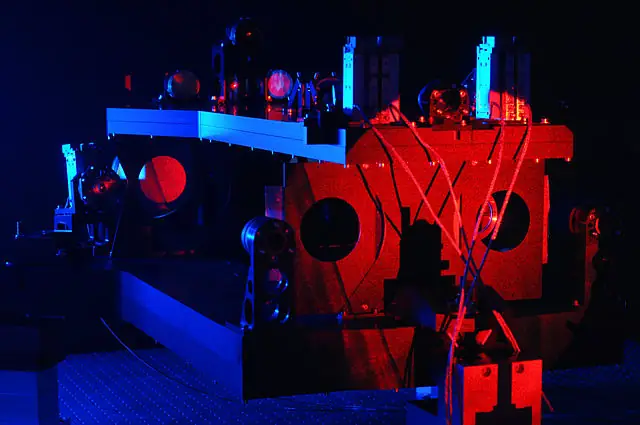
What does the technique of interferometry allow? Since its inception in the late 19th century, interferometry has been revolutionizing various fields of science and engineering.
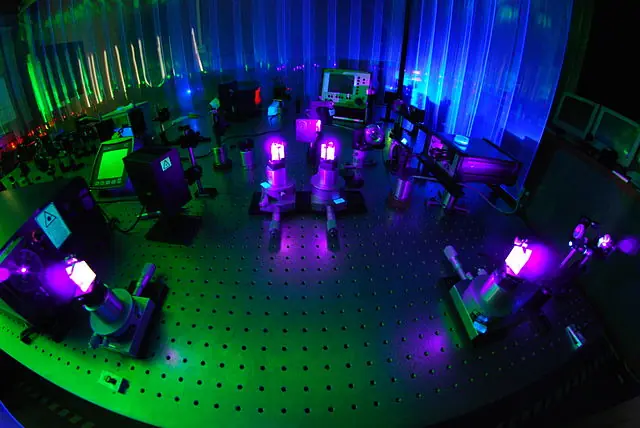

A femtosecond laser is a type of laser that generates extremely short pulses of light, with a duration measured in femtoseconds (1 femtosecond is equal to 10^-15 seconds).
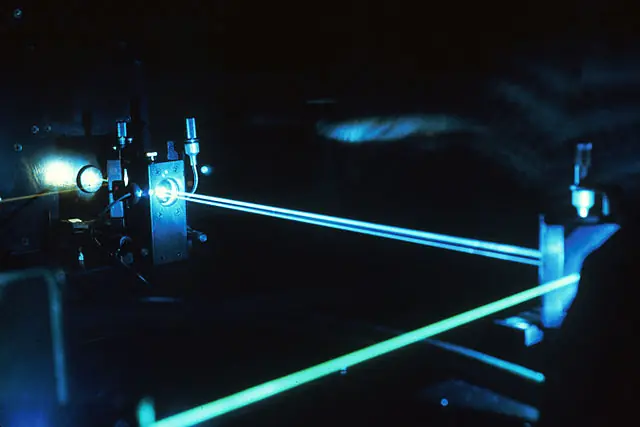
Argon-ion lasers are a type of gas laser that uses an argon plasma to produce light. The first argon-ion laser was built in 1964 by William Bridges at the Hughes Research Laboratories.
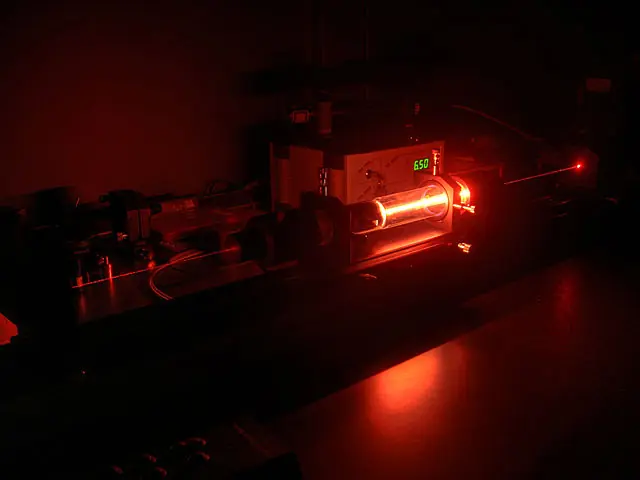
A helium–neon laser is a gas laser using helium and neon as the active medium. The output of a helium–neon laser is a coherent beam of visible light with a wavelength of 632.8 nm, which is in the red region of the visible spectrum.
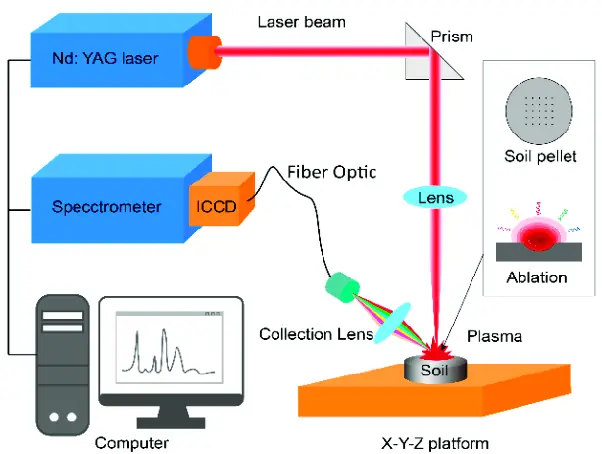
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a powerful analytical technique that has gained popularity in recent years for its ability to provide rapid and non-destructive analysis of a wide range of materials.
End of content
End of content