Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS): An Overview of its Applications and Advantages
This article provides an overview of Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS), a powerful spectroscopic technique used to analyze the elemental composition of materials. We will look at the fundamentals of how LIPS works, the various applications it can be used for, and the advantages it offers over other methods. We will also explore potential future applications of LIPS and its potential to revolutionize the field of spectroscopy.
LIPS is a non-destructive technique that uses laser-induced breakdown of a sample to create a plasma of ions and electrons. This plasma is then subjected to spectroscopic analysis, which allows for the detection of trace elements and the analysis of the elemental composition of the sample. This technique can be used to detect elements in a wide range of materials, from metals to biological samples.
The advantages of LIPS over other methods include its non-destructive nature, high sensitivity, and the ability to analyze a wide range of elements. Additionally, LIPS is relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making it an attractive option for many applications. Some potential applications include the detection of trace elements in materials, the analysis of the elemental composition of samples, and the detection of contaminants.
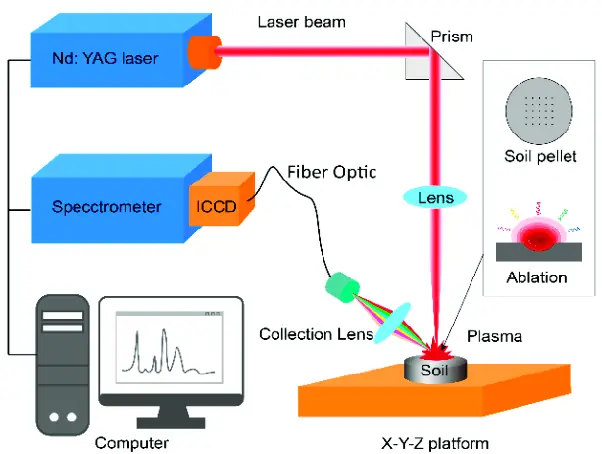
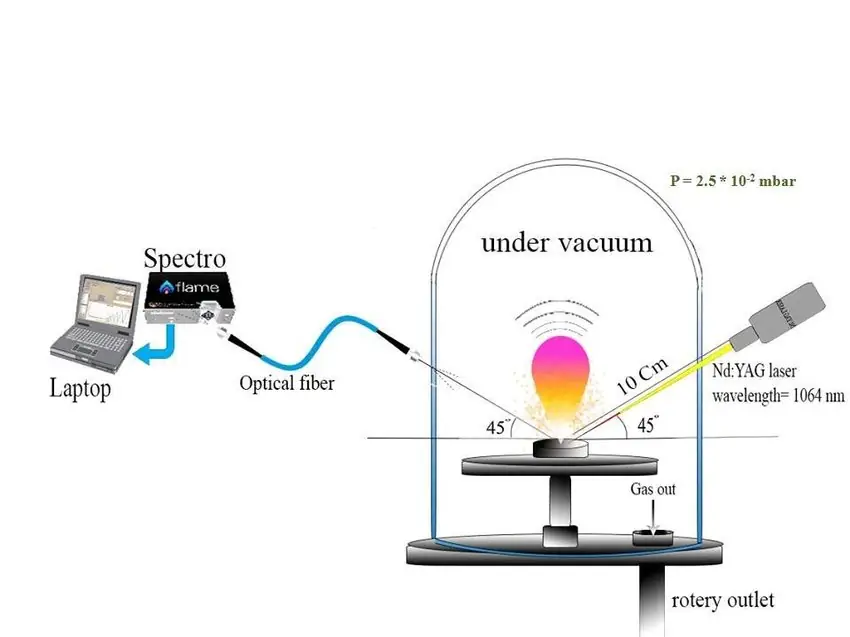
Laser-induced plasma spectroscopy (LIPS) is a technique that combines plasma and spectroscopy. Plasma is a state of matter where atoms are ionized, and spectroscopy is the analysis of light. LIPS works by directing laser pulses to a sample, which causes the sample to become ionized, forming a plasma. This plasma then emits light which is then analyzed to determine the elemental composition of the sample. This technique can be used to detect trace elements in a sample.
The laser pulse used in LIPS is a short pulse of light that is powerful enough to ionize the sample. The light emitted by the plasma is then analyzed to determine the elemental composition of the sample. This analysis is done by measuring the energy of the light emitted by the plasma, which is specific to the elements present in the sample. By measuring the energy of the light, the elemental composition of the sample can be determined.
LIPS is a powerful technique that can be used to detect trace elements in a sample. It is a fast and reliable method for determining the elemental composition of a sample, and can be used in a variety of applications. It is also a non-destructive technique, which means that the sample can be reused after the analysis has been completed.
How LIPS Works
Laser-induced plasma spectroscopy (LIPS) is a technique used to analyze the elemental composition of a sample. It works by using a laser pulse to create a plasma from the sample. The plasma then emits light which is collected and analyzed. This light is broken down into its component elements, allowing for the elemental composition of the sample to be determined. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) can also detect trace elements in the sample. LIPS is a non-destructive technique and has a high sensitivity. This makes it an ideal tool for analyzing the elemental composition of a sample. It is also useful for detecting trace elements, which are often difficult to detect with other techniques.
Applications of Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS)
Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS) is an analytical technique that can be used to analyze the elemental composition of a sample. It is capable of detecting trace elements in a sample, making it highly sensitive in comparison to other methods. LIPS is also a non-destructive method of analysis, meaning that the sample is not damaged or altered during the process. The potential applications of LIPS are vast. It has been used in a variety of industries, including medicine, environmental science, and materials science. For example, LIPS can be used to analyze the composition of air pollution, identify trace elements in pharmaceuticals, and detect the presence of contaminants in food products. Additionally, LIPS has potential for future applications such as analyzing the elemental composition of archaeological artifacts. Despite its many advantages, LIPS is not without its drawbacks. It requires specialized equipment and highly trained personnel to operate, making it expensive to use. Additionally, LIPS is limited by the number of elements it can detect, which is usually limited to elements in the first few rows of the periodic table.
The Advantages of Laser-induced Plasma Spectroscopy (LIPS)
LIPS is a powerful technique for analyzing the elemental composition of materials. It is a non-destructive analysis method, meaning that the samples don’t need to be damaged or altered in order to be studied. This makes it ideal for studying samples that need to remain intact, such as valuable artifacts or delicate biological specimens. The sensitivity of LIPS is also a major advantage. It can detect trace elements that would be undetectable with other methods, making it an invaluable tool for research and industry. It can be used to identify elements in a variety of materials, including metals, alloys, and semiconductors. The potential applications of LIPS are vast. It can be used to identify elements in a variety of contexts, from archeological research to industrial quality control. It can also be used to analyze the elemental composition of air and water samples, which can be invaluable for environmental studies. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that new applications for LIPS will be discovered in the future.