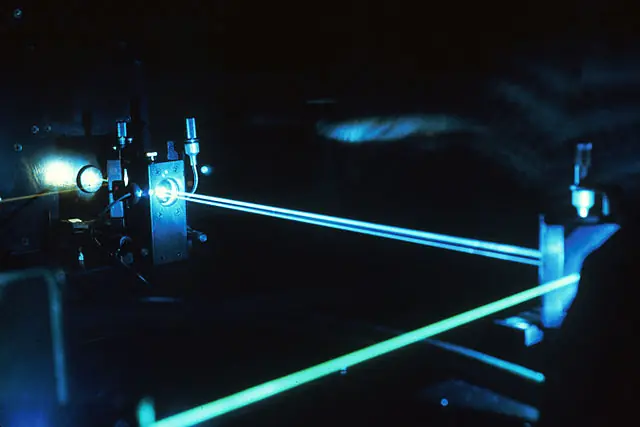
Polarizing and non-polarizing beamsplitter cubes
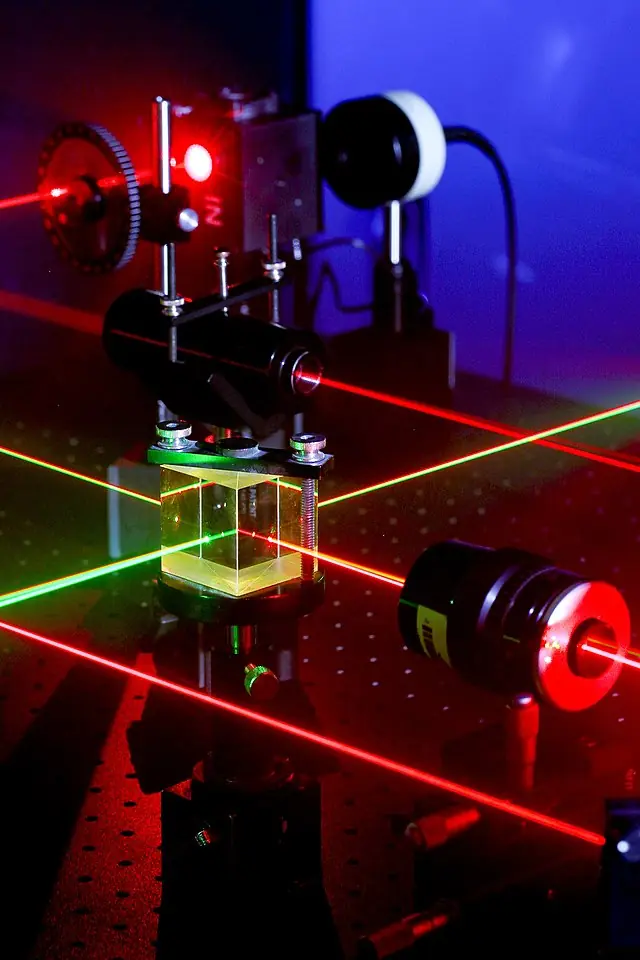
Polarizing beamsplitter cubes (PBSCs) and non-polarizing beamsplitter cubes (NPBSCs) are optical devices that are used to split an incoming light beam into two separate beams. They are often used in a variety of applications, including laser scanning, interferometry, and imaging.
PBSCs are designed to split light based on its polarization. Polarization refers to the direction in which light waves oscillate as they travel through space. When light is polarized, its oscillations are all in the same direction, while non-polarized light has oscillations in all directions.
PBSCs are made up of two perpendicular crystal plates, called polarizers, which are coated with a thin layer of dichroic material. When light hits the PBSC, it is split into two beams, one with horizontal polarization and one with vertical polarization. The dichroic material reflects the horizontally polarized light, while the vertically polarized light is transmitted through the cube.
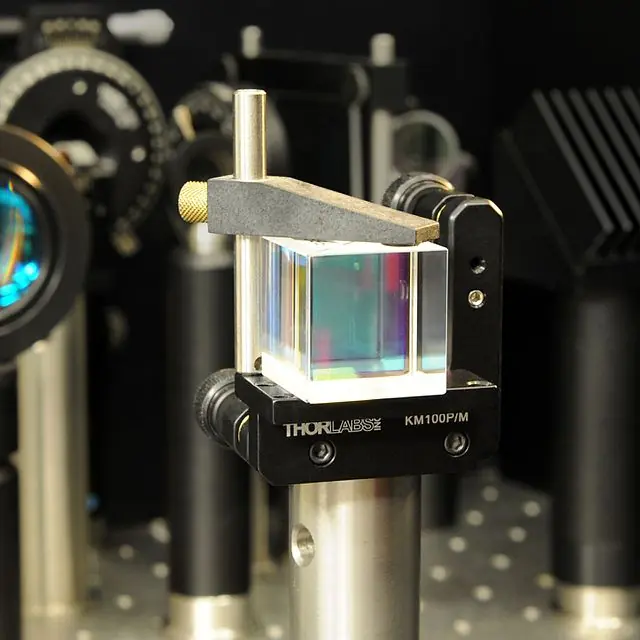
NPBSCs, on the other hand, do not split light based on polarization. Instead, they use a combination of reflection and transmission to split the incoming light beam into two equal intensity beams. NPBSCs are made up of two parallel crystal plates coated with a thin layer of dichroic material. When light hits the NPBSC, half of it is reflected off the top surface, while the other half is transmitted through the cube.
In conclusion, PBSCs and NPBSCs are important optical devices that are used to split incoming light beams into two separate beams. PBSCs split light based on its polarization, while NPBSCs split light using a combination of reflection and transmission. Both types of beamsplitter cubes are widely used in a variety of applications and play a crucial role in the field of optics.