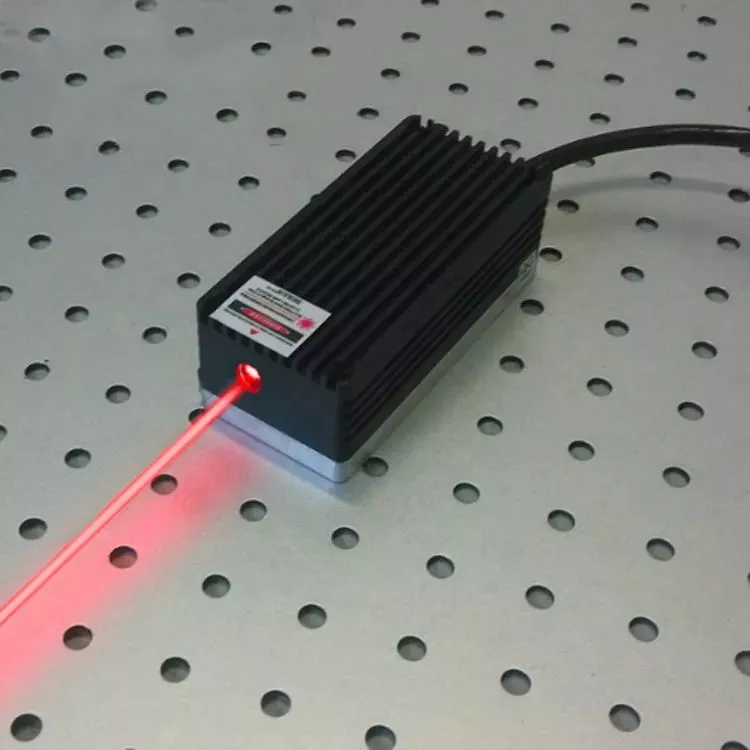
Diode Pumped Solid State (DPSS) Lasers

A diode pumped solid state (DPSS) laser is a type of solid state laser that uses an optical diode to pump a solid gain medium. The pump diode emits light at a wavelength that is absorbed by the gain medium, which then amplifies the light and emits it at a different wavelength. DPSS lasers are used in a variety of applications, including medical therapies, material processing, and spectroscopy.
The basic principle of a DPSS laser is similar to that of other lasers, such as gas lasers and fiber lasers. A DPSS laser includes a gain medium, a pumping source, and an optical resonator. The gain medium is a material that amplifies light, while the pumping source provides energy to the gain medium. The optical resonator confines and amplifies the light emitted by the gain medium.

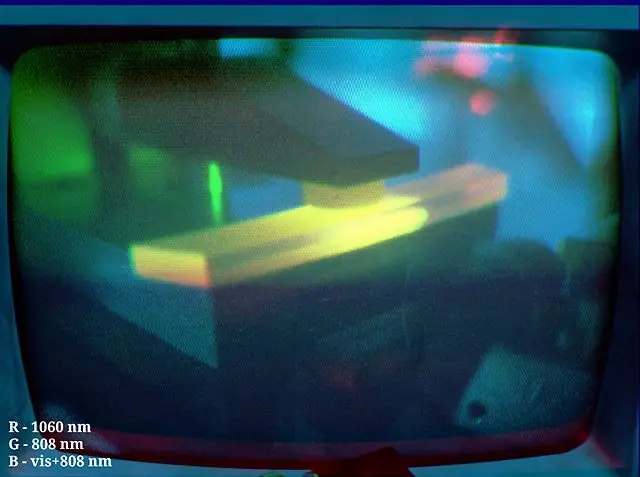
The gain medium of a DPSS laser is typically a solid, such as a crystal or a glass rod. The most common gain medium used in DPSS lasers is neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG). Nd:YAG is a solid that can be pumped with light at a wavelength of 808 nm. When Nd:YAG is pumped with 808 nm light, it emits light at a wavelength of 1064 nm.
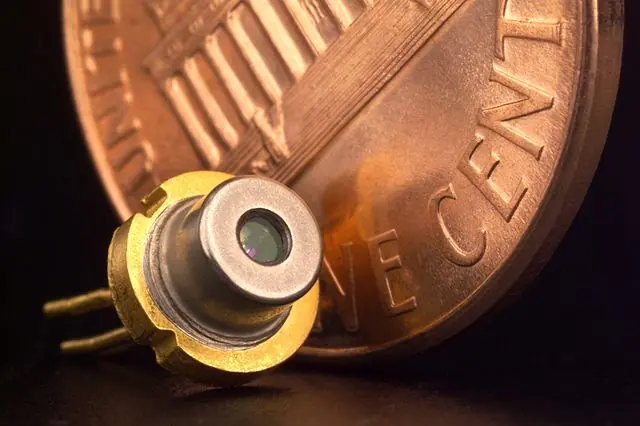
The pumping source of a DPSS laser is usually a laser diode. Laser diodes are semiconductor devices that emit light when a current is passed through them. The light emitted by a laser diode is monochromatic, meaning it is a single color. DPSS lasers typically use laser diodes that emit light at a wavelength of 808 nm.
The optical resonator of a DPSS laser is typically a mirror, or a combination of mirrors. The resonator confines and amplifies the light emitted by the gain medium. The resonator also provides feedback to the gain medium, which amplifies the light.
DPSS lasers are classified as continuous wave (CW) or pulsed. CW DPSS lasers emit a continuous beam of light, while pulsed DPSS lasers emit light in short pulses. Pulsed DPSS lasers are used in applications where a high peak power is required, such as in medical therapies.
DPSS lasers are also classified by the type of resonator they use. The most common type of resonator used in DPSS lasers is the standing wave resonator. Standing wave resonators are made of two mirrors, one of which is partially transparent. The light emitted by the gain medium is reflected back and forth between the mirrors, and is amplified each time it passes through the gain medium.

DPSS lasers can also be made with a traveling wave resonator. In a traveling wave resonator, the light emitted by the gain medium travels in one direction through the resonator. The light is amplified as it passes through the gain medium, and is reflected back and forth between the mirrors of the resonator.
The output of a DPSS laser can be further increased by using multiple gain mediums. This is known as a multi-pass amplifier. In a multi-pass amplifier, the light emitted by the gain medium is reflected back and forth between a series of mirrors. The light passes through the gain medium multiple times, and is amplified each time it passes through the gain medium.
DPSS lasers are used in a variety of applications, including medical therapies, material processing, and spectroscopy. DPSS lasers are commonly used in medical therapies because they can be used to generate short pulses of high-energy light. This high-energy light can be used to destroy cancerous cells or to remove tattoos.