Tunable Orange-Red Diamond Laser Revolutionizes Biomedicine, Astronomy and Spectroscopy
Tunable Orange-Red Diamond Laser transforms Biomedicine, Astronomy and Spectroscopy with its unique capabilities.
The latest news about lasers, find out about the newest developments in semiconductor laser diodes, laser safety legislation, and more.
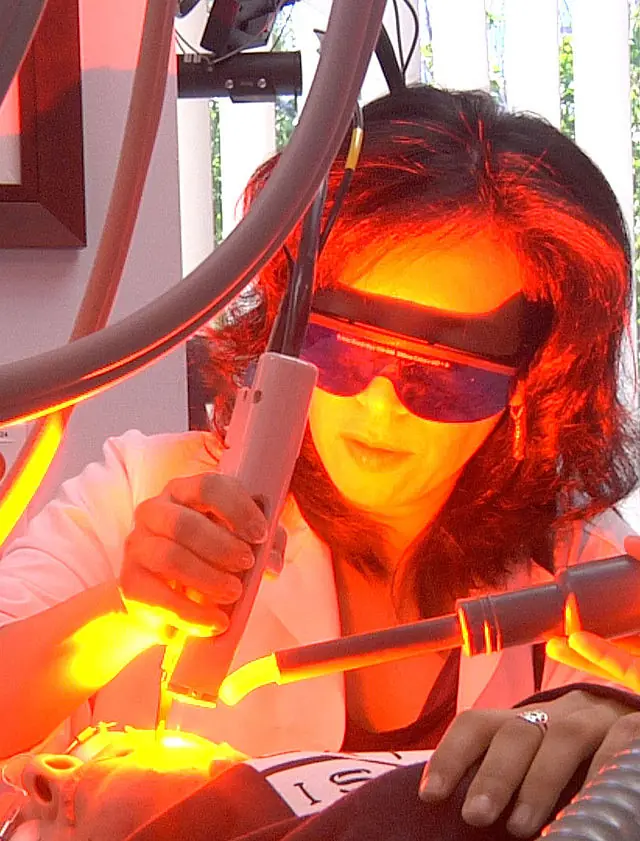

Tunable Orange-Red Diamond Laser transforms Biomedicine, Astronomy and Spectroscopy with its unique capabilities.
The world of optical fiber sensing just took a big leap forward with the creation of an ultracompact microinterferometer-based fiber Bragg grating interrogator on a silicon chip.
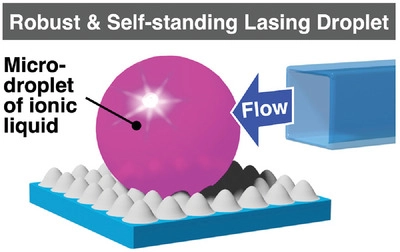
A new type of laser has been developed by scientists from the Tsukuba Research Center for Energy Materials Science at the University of Tsukuba that is both robust in air and tunable by airflow.
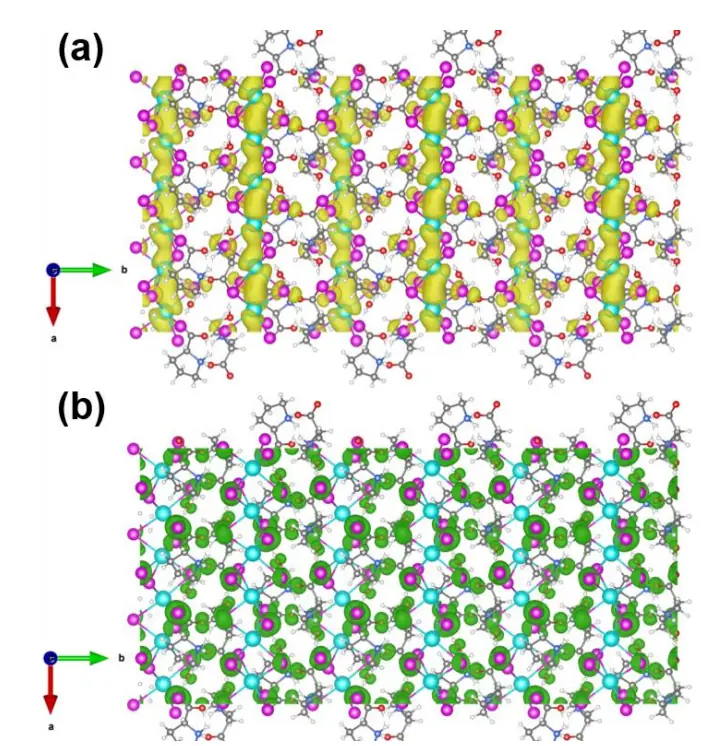
Chiral hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) with intrinsic noncentrosymmetry have shown great potentials for chiroptoelectronic applications including second-order nonlinear optics (NLO).
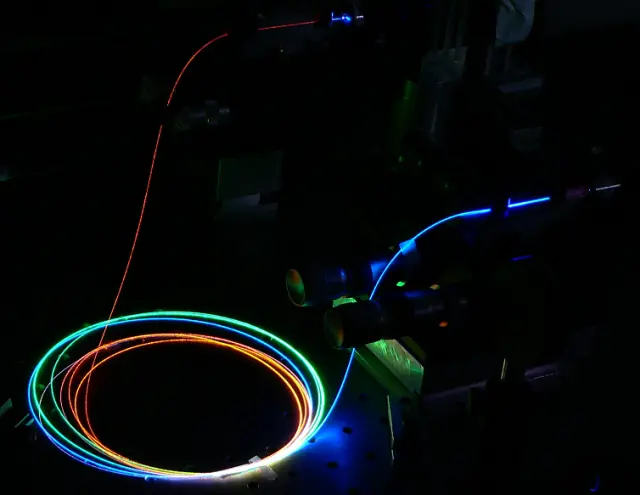

A passively Q-switched mode-locked fiber laser operating at a fundamental repetition rate of 1 GHz has been demonstrated using Yb-Mg-doped silica glass as a laser medium, overcoming photodarkening effects and offering potential applications in optical frequency combs, bio-optical imaging, light communication, material processing, and microfabrication.
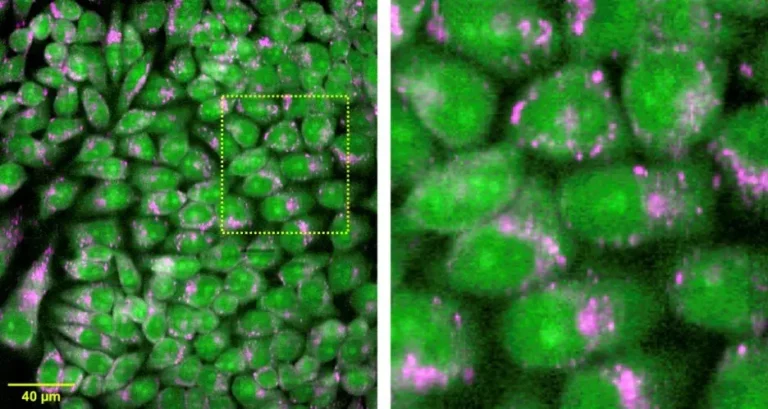
A research team from Osaka University has developed a high-throughput Raman microscope that can acquire information hundreds of times faster than a conventional Raman microscope.
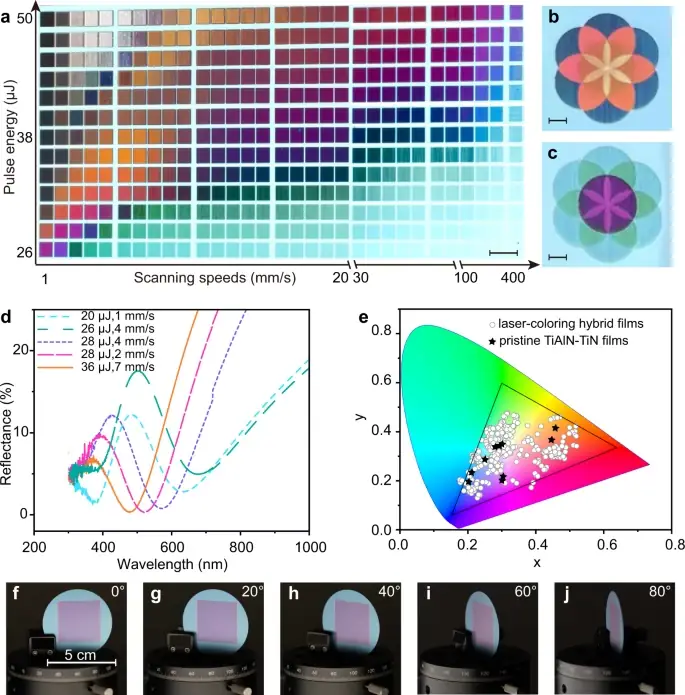
A new laser printing technique offers wide-gamut, high-resolution, and high-speed printing with long-term stability and viewing-angle independence.
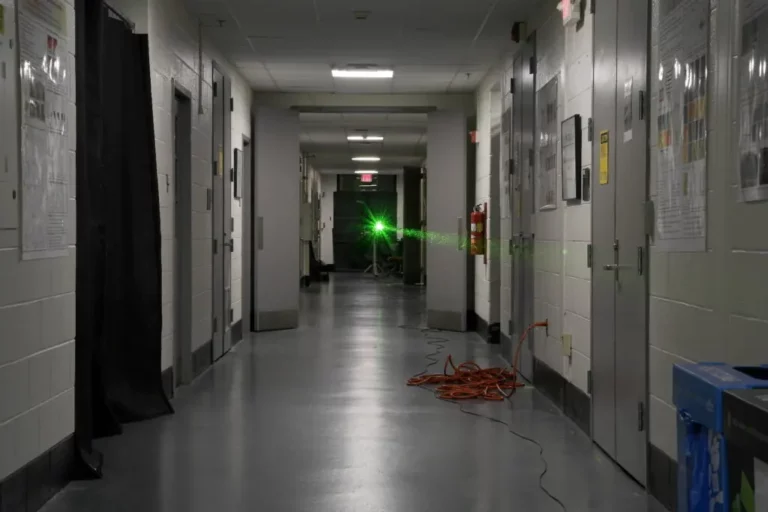

A team of researchers at the University of Maryland’s Energy Research Facility has set a record for guiding light in 45-meter-long air waveguides.
Researchers from the University of Strathclyde have developed laser-driven ‘plasma mirrors’ that are capable of reflecting or manipulating light.
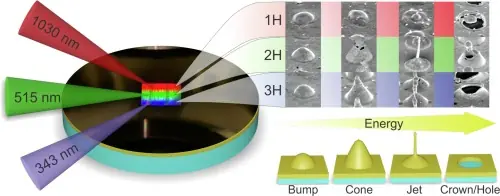
In a recent study, the formation of gold nanobumps, nanocones, and nanojets using laser direct writing techniques was investigated using different laser wavelengths. The results showed that the wavelength of the laser used impacts the size and shape of the formed structures, making the laser wavelength an important factor to consider when creating plasmonic nanostructures.
End of content
End of content