What is Laser Linewidth?
Laser linewidth is a term that is used to describe the spectral width of a laser beam. It is a measure of the range of wavelengths that are emitted by the laser, and is typically expressed in units of nanometers (nm). The laser linewidth is an important parameter in laser technology, as it determines the precision and accuracy of the laser’s wavelength, and can have a significant impact on the performance of a laser system.
The spectral width of a laser beam is determined by the coherence of the laser light. Coherence refers to the degree to which the waves of light are in phase with each other. A laser beam with a narrow spectral width will have a high degree of coherence, meaning that the waves of light are all in phase with each other. This results in a laser beam with a high level of intensity and a well-defined wavelength. On the other hand, a laser beam with a wide spectral width will have a lower degree of coherence, meaning that the waves of light are not all in phase with each other. This results in a laser beam with a less well-defined wavelength.
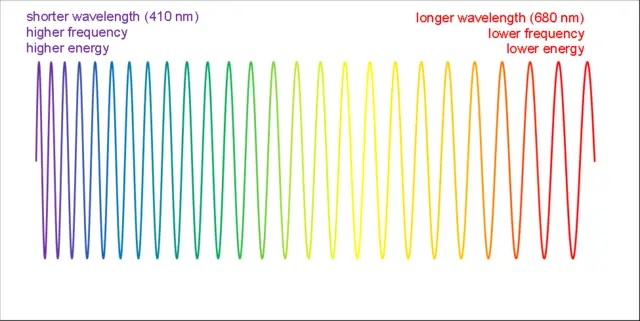
The spectral width of a laser beam can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of laser, the pumping mechanism, and the quality of the resonator cavity. For example, lasers that use a mode-locked pumping mechanism, such as a mode-locked laser diode, typically have a narrow spectral width, as the mode-locking process results in a high degree of coherence. On the other hand, lasers that use a continuous pumping mechanism, such as a continuous wave (CW) laser diode, typically have a wider spectral width, as the pumping process does not result in a high degree of coherence.
The laser linewidth is an important parameter in a variety of applications, including spectroscopy, imaging, and precision measurement. In spectroscopy, the laser linewidth determines the resolution of the instrument, as a narrower linewidth allows for the detection of smaller differences in wavelength. In imaging, the laser linewidth determines the accuracy of the image, as a narrower linewidth allows for more precise targeting of specific wavelengths. In precision measurement, the laser linewidth determines the accuracy of the measurement, as a narrower linewidth allows for more precise measurement of wavelengths.
Overall, the laser linewidth is an important parameter in laser technology, as it determines the precision and accuracy of the laser’s wavelength. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of laser, the pumping mechanism, and the quality of the resonator cavity, and has a significant impact on the performance of a laser system. Understanding and controlling the laser linewidth is essential for optimizing the performance of laser systems in a variety of applications.