Industrial Lasers: The Future in Material Processing

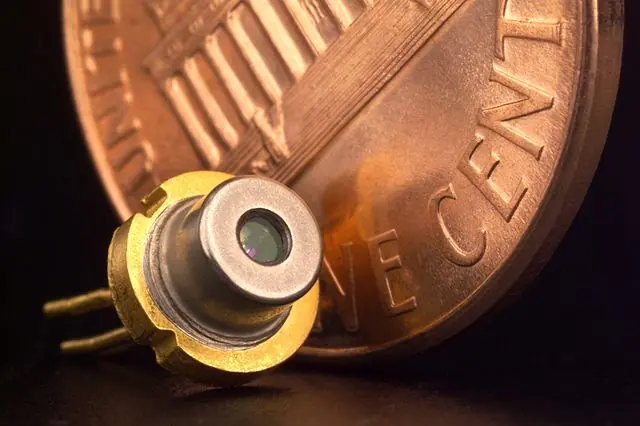
Lasers have been used in industrial settings for decades, but their use has been largely limited to cutting and welding applications. However, recent advances in laser technology are beginning to open up new possibilities for using lasers in a wide range of material processing applications.
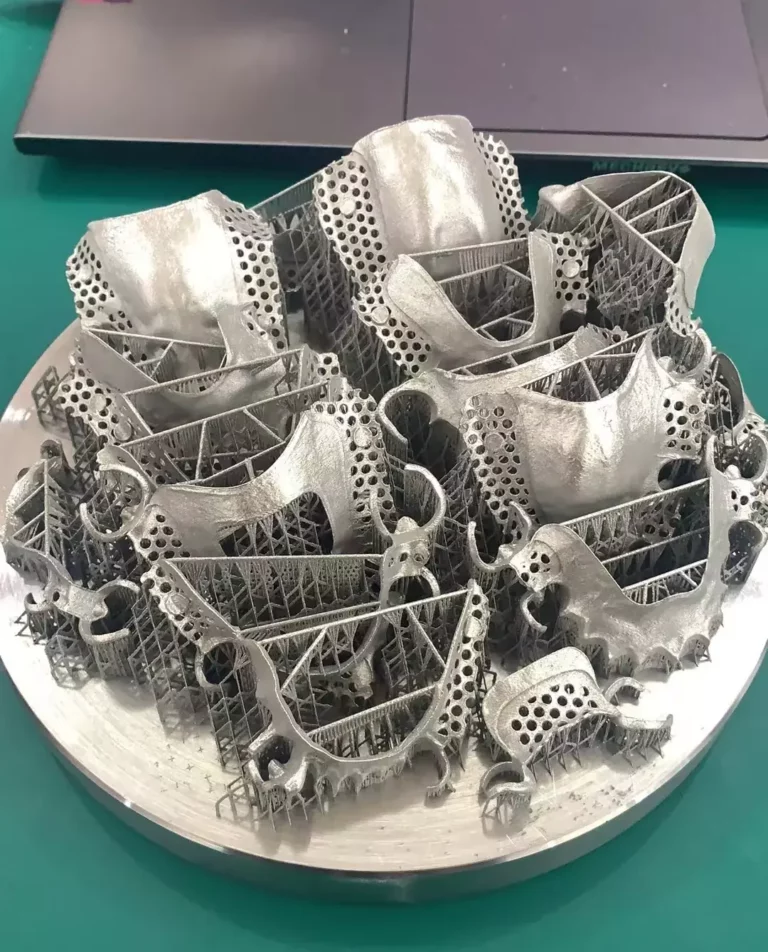
One of the most promising areas for the use of lasers is in the field of 3D printing. Laser-based 3D printers are able to create highly detailed and complex objects from a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. This technology is already being used to create prototypes and small-scale production runs of parts and products.
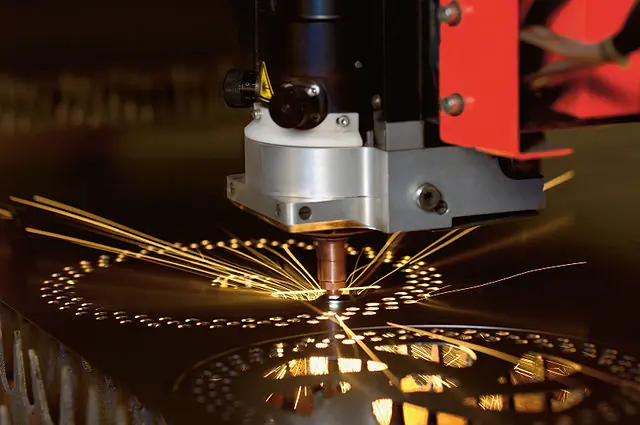
Another area where lasers are beginning to make an impact is in the realm of sheet metal fabrication. Lasers can be used to cut, drill, or etch patterns into metal sheets with incredible precision. This allows manufacturers to create parts with very tight tolerances without the need for expensive tooling.
Lasers are also being used more frequently for surface treatment applications such as hardening, tempering, and annealing. By carefully controlling the laser’s power output and beam profile, it is possible to selectively heat specific areas of a workpiece without causing damage to surrounding materials. This makes lasers an ideal tool for heat treating delicate components made from sensitive materials.

There are a variety of different laser technologies that are used in industrial settings, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
CO2 lasers are the most common type of laser used in industrial applications. They are relatively inexpensive and can be used to cut a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. However, CO2 lasers have a relatively low power output and are not well suited for surface treatment applications.
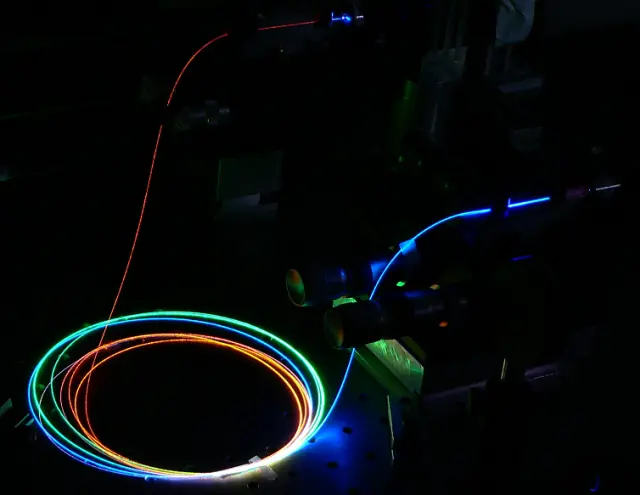
Fiber lasers are another popular type of laser used in industry. They offer several advantages over CO2 lasers, including higher power output, better beam quality, and the ability to operate at shorter wavelengths. This makes them ideal for cutting thicker materials and for surface treatment applications such as hardening and tempering.
YAG lasers are another type of laser that is often used in industrial settings. YAG lasers offer high power output and good beam quality, making them well suited for cutting and welding applications. However, they are not as widely used as fiber or CO2 lasers due to their relatively high cost.
As laser technology continues to evolve, there is no doubt that it will find even more uses in industrial settings. The precise control that lasers offer opens up a world of possibilities for improving manufacturing efficiency and quality while reducing costs.