Femtosecond Laser Cataract Surgery: A Comprehensive Guide
Cataracts, the clouding of the natural lens in the eye, are a leading cause of vision loss worldwide. Traditionally, cataract surgery has involved manual techniques to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). However, recent advancements in technology have led to the development of a new, more precise method: femtosecond laser cataract surgery. This article will provide an in-depth look at this revolutionary procedure and its potential impact on the field of ophthalmology.
Femtosecond Lasers: The Basics
Definition and key features
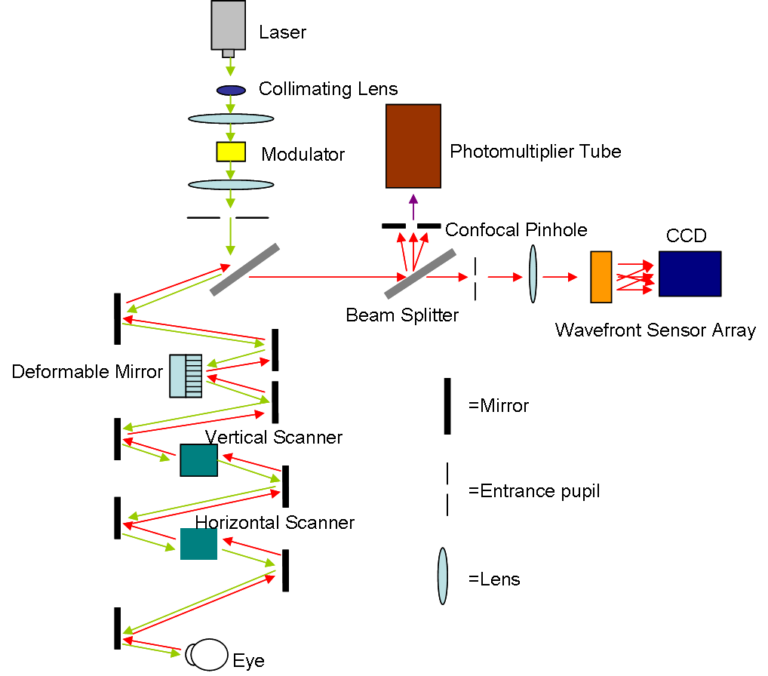
Femtosecond lasers are a type of ultrafast pulsed lasers that emit light in extremely short bursts, with each pulse lasting just one quadrillionth of a second, or a femtosecond. These lasers have several key features, such as high peak power, precision, and minimal thermal damage, which make them suitable for a range of applications across various fields.
How femtosecond lasers work
Femtosecond lasers generate light pulses through a process called mode-locking, which synchronizes the light waves within the laser cavity to produce a train of ultrashort pulses. The rapid succession of pulses allows for the delivery of high energy in an incredibly short amount of time, enabling precise and controlled ablation or cutting of target tissue without causing significant collateral damage to surrounding structures.
Applications of femtosecond lasers in medicine
The unique properties of femtosecond lasers have opened up numerous possibilities in medicine, particularly in the field of ophthalmology. Some notable applications include:
- LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis): Femtosecond lasers have been used in LASIK surgery to create precise corneal flaps, improving the safety and outcomes of the procedure.
- Corneal transplantation: The accuracy of femtosecond lasers allows for the creation of custom-shaped corneal grafts, improving the success rate and visual outcomes of corneal transplants.
- Intrastromal corneal ring segment (ICRS) implantation: Femtosecond lasers can create precise channels in the cornea for the placement of ICRS, a treatment option for keratoconus and other corneal ectasias.
- Glaucoma surgery: Femtosecond lasers are being explored for their potential use in minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries, aiming to improve treatment outcomes and reduce complications.
In addition to ophthalmology, femtosecond lasers have also found applications in other medical fields, such as dentistry (for hard and soft tissue ablation), neurosurgery (for precise cutting of brain tissue), and dermatology (for skin resurfacing and scar revision).
Advancements in Cataract Surgery
Cataract surgery has experienced a remarkable evolution since its early days, with constant improvements in techniques and technology contributing to better outcomes for patients. This section will explore the progression of cataract surgery, highlighting the advantages of laser-assisted procedures and the emergence of femtosecond laser cataract surgery as a cutting-edge option.
Evolution of cataract surgery techniques
- Early methods: The history of cataract surgery dates back thousands of years, with early techniques involving a procedure called “couching,” where the lens was dislodged and pushed into the vitreous cavity, resulting in only limited visual improvement.
- Intracapsular cataract extraction (ICCE): For many years, ICCE was the standard cataract surgery technique. It involved the removal of the entire lens capsule along with the cloudy lens. However, this method had high complication rates, including retinal detachment and glaucoma.
- Extracapsular cataract extraction (ECCE): ECCE marked an improvement over ICCE, as it involved removing only the lens while leaving the posterior capsule intact. This approach reduced complications and allowed for the implantation of an IOL within the capsule.
- Phacoemulsification: Developed in the 1960s, phacoemulsification revolutionized cataract surgery. The procedure uses ultrasound energy to break the lens into small fragments, which are then aspirated through a small incision. This method offers quicker recovery times and fewer complications compared to earlier techniques.
Advantages of laser-assisted cataract surgery
Laser-assisted cataract surgery emerged in the 21st century as an innovative alternative to traditional techniques. Utilizing lasers such as the femtosecond laser, this method offers several advantages:
- Precision: Lasers allow for more accurate incisions and capsulotomies, reducing the risk of complications and improving visual outcomes.
- Reduced energy: Laser-assisted cataract surgery requires less ultrasound energy during lens fragmentation, which can minimize potential damage to the surrounding eye structures.
- Customization: Laser technology enables personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique eye anatomy and cataract characteristics.
Emergence of femtosecond laser cataract surgery
Femtosecond laser cataract surgery has emerged as a promising advancement in the field of ophthalmology, building upon the benefits of laser-assisted cataract surgery. This procedure utilizes the ultrafast, high-precision femtosecond laser to perform key steps of the surgery, including corneal incisions, anterior capsulotomies, and lens fragmentation. As a result, femtosecond laser cataract surgery has the potential to further improve surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.

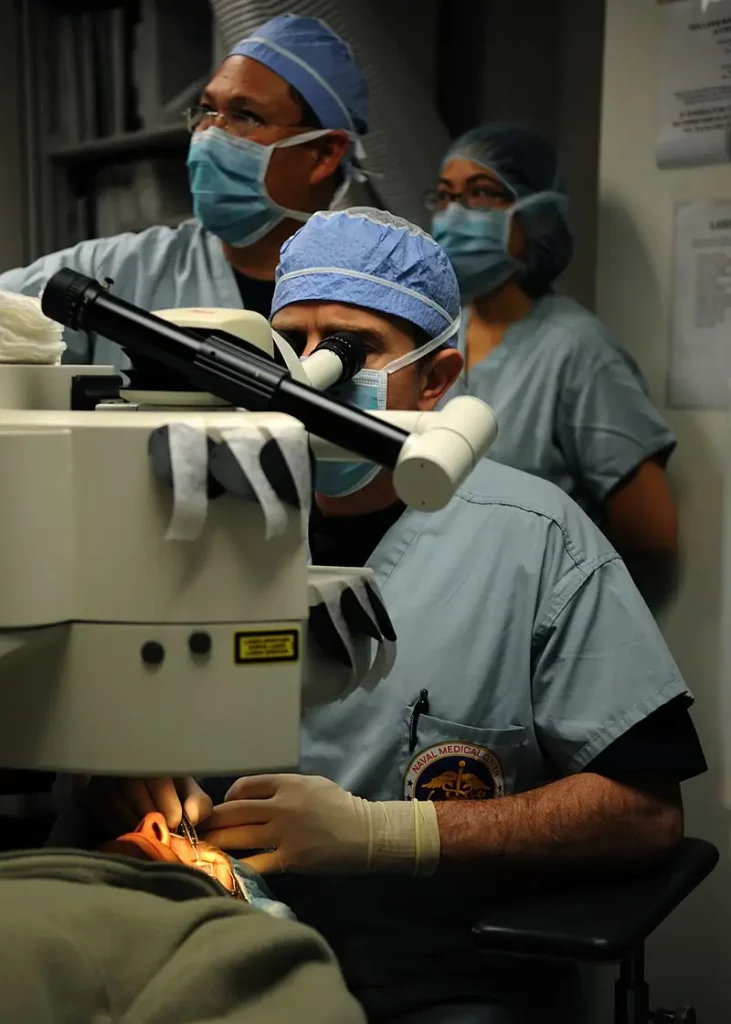
The Femtosecond Laser Cataract Surgery Procedure
Preoperative assessment Before undergoing femtosecond laser cataract surgery, patients receive a thorough eye examination to determine the type and severity of their cataract, as well as the appropriate IOL prescription.
The surgical process
- Corneal incision: The femtosecond laser is used to create precise, self-sealing incisions in the cornea, allowing access to the lens.
- Anterior capsulotomy: The laser creates a perfectly circular opening in the front of the lens capsule, providing access to the cataract.
- Lens fragmentation: The laser breaks the cataract into smaller pieces, making it easier to remove.
- Lens removal and implantation of intraocular lens (IOL): The cataract fragments are removed, and the IOL is inserted into the lens capsule.
Postoperative care and follow-up Patients typically experience minimal discomfort and can often return to their normal activities within a day or two. Regular follow-up appointments ensure proper healing and optimal visual outcomes.
Benefits of Femtosecond Laser Cataract Surgery
Femtosecond laser cataract surgery offers several advantages over traditional methods, including improved precision and accuracy, enhanced safety and reduced complications, customization and individualized treatment, and faster recovery times. These benefits have made the procedure increasingly popular among both patients and ophthalmologists.
Potential Risks and Complications
While femtosecond laser cataract surgery is generally considered safe, it is not without risks. Common risks associated with cataract surgery include infection, inflammation, and retinal detachment. Specific risks related to femtosecond laser technology include corneal burns and incomplete capsulotomy. However, these complications are rare and can be managed effectively with prompt medical intervention.
Comparing Femtosecond Laser Cataract Surgery to Traditional Methods
When compared to traditional methods such as phacoemulsification and manual capsulorhexis, femtosecond laser cataract surgery offers improved outcomes and higher patient satisfaction. The procedure may also be more cost-effective in the long run, as it can reduce the need for additional corrective surgeries and minimize postoperative complications.
The Future of Femtosecond Laser Cataract Surgery
Ongoing research and development As femtosecond laser technology continues to advance, researchers are exploring new ways to improve and refine the cataract surgery process. This includes the development of even more precise lasers and the integration of advanced imaging techniques.
Integration with advanced diagnostic tools Combining femtosecond laser cataract surgery with other diagnostic tools, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and wavefront aberrometry, has the potential to further enhance surgical outcomes by providing a more comprehensive view of the eye and enabling better customization of the procedure.
Potential applications in other ocular surgeries Femtosecond laser technology is not limited to cataract surgery. Its potential applications extend to other ocular surgeries, such as refractive surgery, glaucoma treatment, and corneal transplantation. As the technology continues to advance, it is likely that femtosecond lasers will play an increasingly important role in ophthalmology.
Conclusion
Femtosecond laser cataract surgery represents a significant advancement in the field of ophthalmology, offering patients a more precise, safer, and customized treatment option. While there are still potential risks and complications associated with the procedure, ongoing research and innovation will likely continue to improve its safety and efficacy. It is essential for patients to explore their options and consult with their ophthalmologists to determine the best course of action for their specific needs. As femtosecond laser technology continues to evolve, it is poised to have a lasting impact on the way cataract surgery is performed and, ultimately, on the quality of life for millions of people around the world.