Pulse Compression Gratings: Exploring the Physics, Mechanics, and Applications
Pulse compression gratings are optical devices used to modify the temporal characteristics of a light pulse.
This category covers topics such as wave and particle properties of light, geometrical optics, polarization, diffraction, and optical instruments like microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
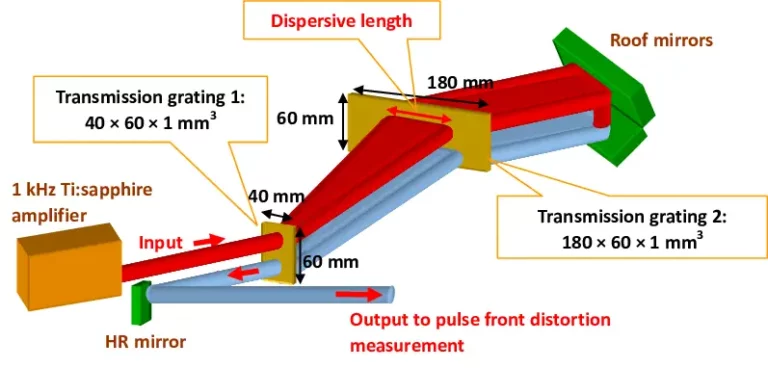
Pulse compression gratings are optical devices used to modify the temporal characteristics of a light pulse.

An anti-reflective coating, also known as an AR coating or non-reflective coating, is a thin layer of material applied to the surface of a lens or other optical element in order to reduce the amount of light that is reflected off of it.
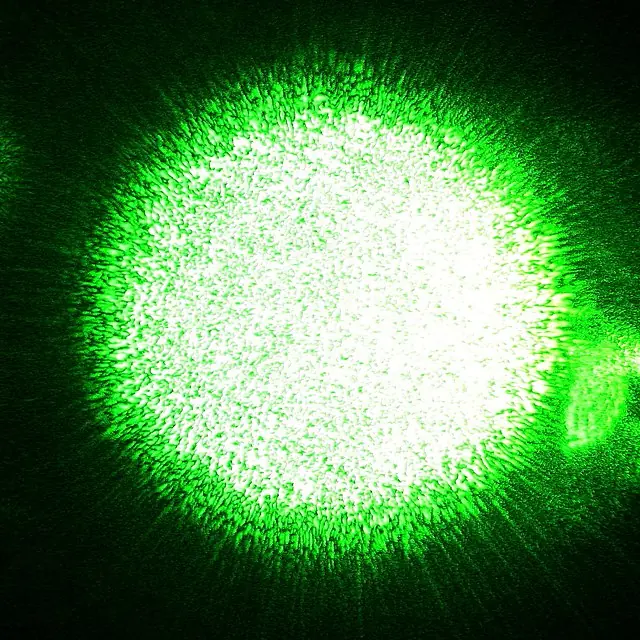
Laser speckle is a phenomenon that occurs when laser light is scattered by a rough or irregular surface or by a medium with inhomogeneities, such as a turbid fluid.
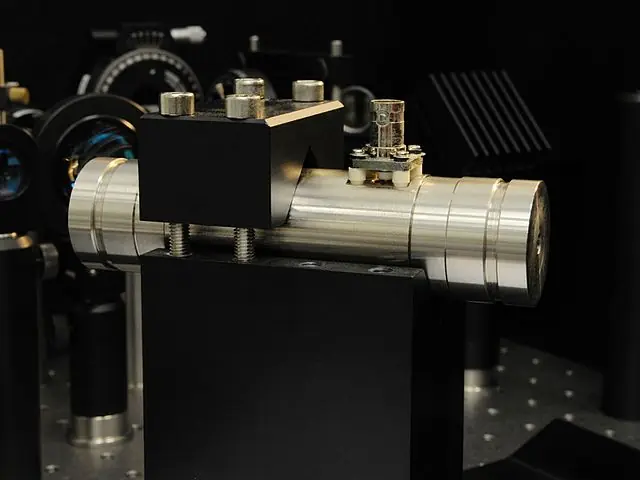
A laser etalon is a device that is used to accurately measure the frequency of a laser beam. It works by using the principle of interference, which occurs when two waves meet and either reinforce or cancel each other out.
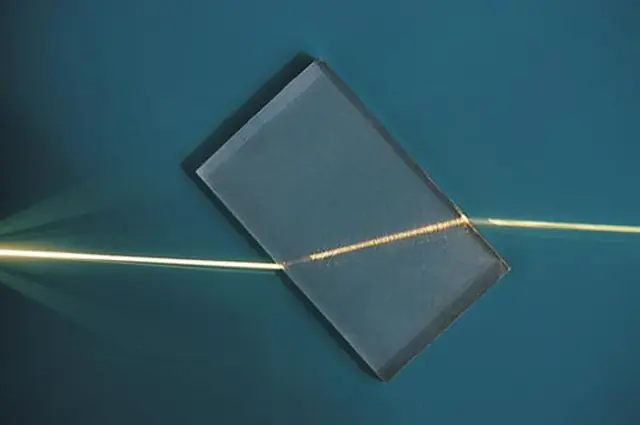
Gradient-index (GRIN) optics are a type of optical technology that uses lenses or optical fibers with a refractive index that varies in a continuous and gradual manner.
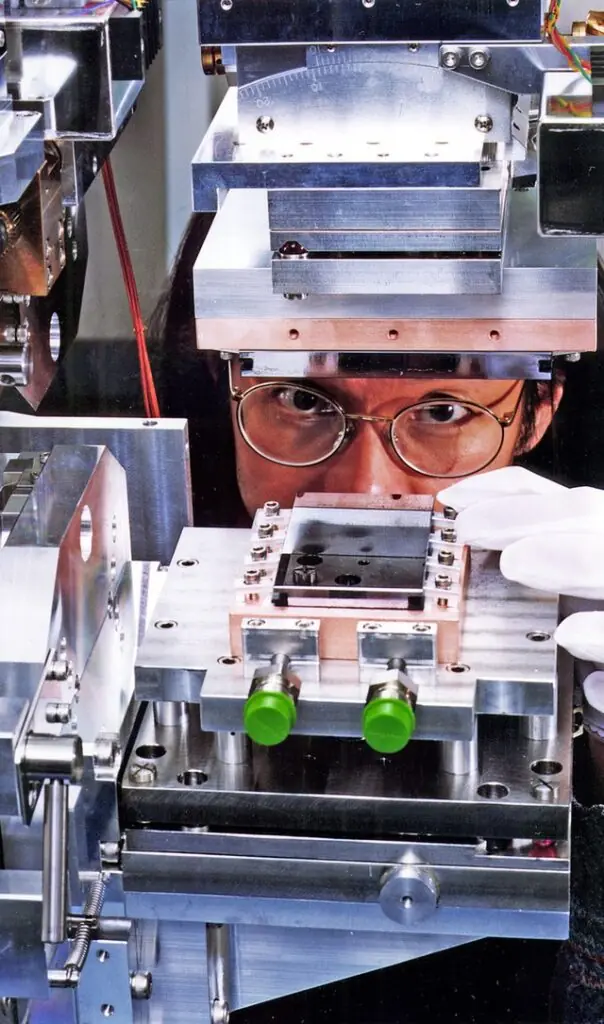
A monochromator is a device used to select and isolate a single wavelength of light from a broader spectrum.

In this article, we will explore the different types of laser beam steering techniques and their applications.
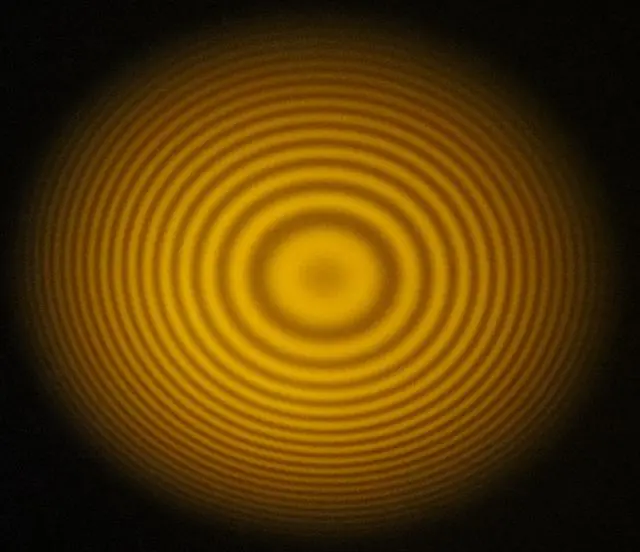
A scanning Fabry-Perot interferometer is a device that is used to measure the properties of light and to analyze the properties of materials.

A wave plate, also known as a phase retarder, is a type of optical device that is used to alter the phase of light waves.
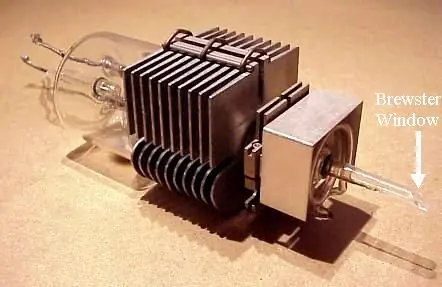
Brewster window, named after Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster, is a type of optical window that is commonly used in scientific and industrial applications.
End of content
End of content